The Primary School Curriculum
Primary education consists of an eight year cycle: junior infants, senior infants, and first to sixth classes. A redeveloped Primary School Curriculum has now been published and will be introduced to all primary and special schools in the coming years.
Primary Curriculum Framework
The Primary Curriculum Framework forms the basis for high-quality learning, teaching, and assessment for all children attending primary and special schools. It reflects our shared understanding of, and trust in, the many positive features of education in our primary and special schools while providing the blueprint for guiding the enhancement of primary and special education for the coming years. Use the tabs below to explore aspects of the Primary Curriculum Framework or access the full document and frequently asked questions.

Vision
The curriculum aims to provide a strong foundation for every child to thrive and flourish, supporting them in realising their full potential as individuals and as members of communities and society during childhood, as they progress through primary and special education and into post-primary education. Building on their previous experiences, the curriculum views children as unique, competent, and caring individuals, and it views teachers as committed, skilful, and agentic professionals
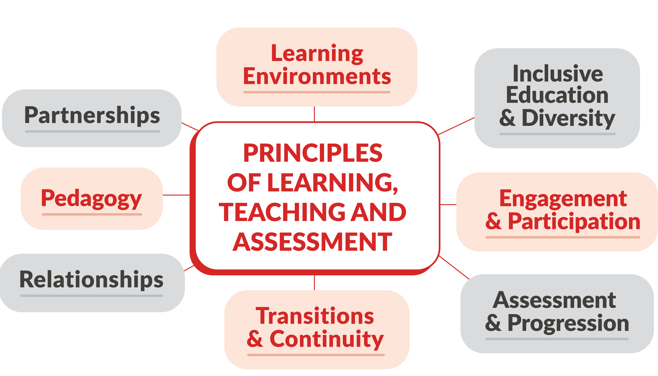
Principles of Learning, Teaching and Assessment
There are eight overarching principles that schools need to consider in pursuing the curriculum vision. The principles convey what is valued in primary and special education and what lies at the heart of high-quality learning, teaching, and assessment in the primary curriculum. Read more about each of the principles below.
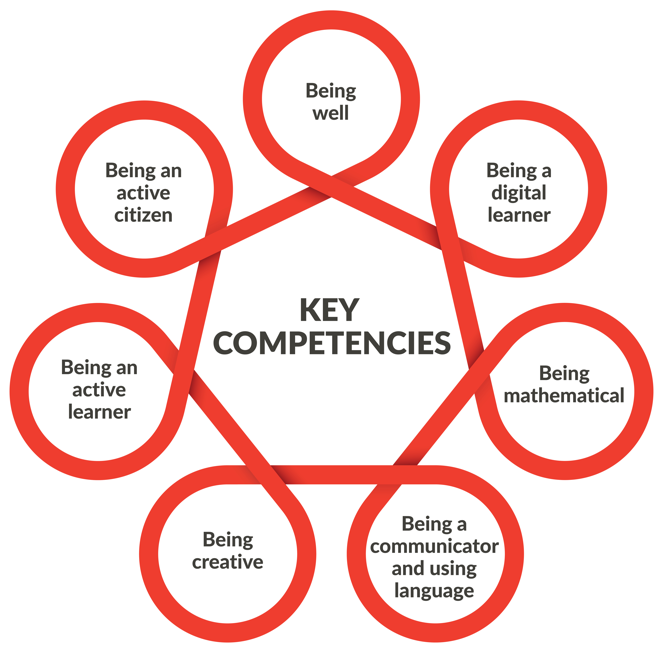
Key Competencies
Seven Key Competencies for children are embedded to foster deep learning and contribute to holistic development. The seven key competencies, because of their interconnecting nature, support the curriculum’s vision of empowering children to act and make decisions in relation to specific learning experiences, events, and situations.
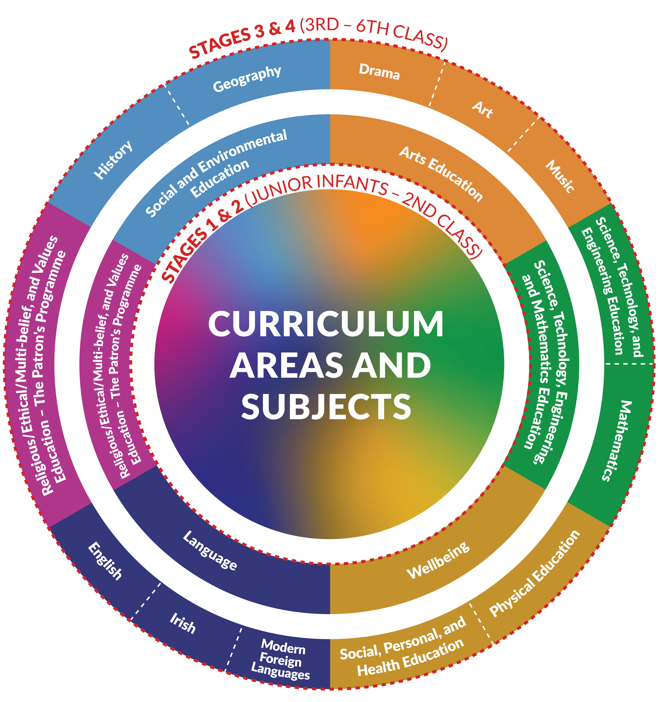
Curriculum Areas and Subjects
The curriculum is presented in five broad curriculum areas:
- Language
- Science, Technology, Engineering, and
Mathematics (STEM) Education - Wellbeing
- Arts Education
- Social and Environmental Education.
The curriculum areas become more differentiated by subjects as children move through the primary classes. In addition to the five areas, school patrons have a legal right to design their own programme in accordance with the ethos of their school. Use the tabs below to learn more about each curriculum area or visit our curriculum online site to see the full specifications.
- Language
- Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths (STEM) Education
- Wellbeing
- Arts Education
- Social and Environmental Education
- Time Allocations
Language learning enables children to understand the world around them and to communicate effectively with others. Communication takes many forms and is often multimodal. Exposure to a wide variety of texts fosters children’s appreciation for and enjoyment of literature from different cultures. Language enables children to engage emotionally, socially, cognitively, imaginatively, and aesthetically in relationships and cultural experiences. Providing children with opportunities to be creative through language fosters a sense of enjoyment in their language learning. The curriculum acknowledges the language learning journeys that all children are on in English and Irish. It also acknowledges and harnesses the diversity of languages, including Irish Sign Language, used in Irish primary and special schools. It supports the introduction of modern foreign languages in stages 3 and 4, incrementally building on children’s existing knowledge and awareness of language and progressing from a language awareness model to a competency model in stage 4.
Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Education supports children’s capacity to understand and engage fully with the world around them. Mathematics provides the foundation for science, technology, and engineering and is the study of the relationships, connections, and patterns that surround us. Science, technology, and engineering are intrinsically linked and enable children to benefit from learning about and working with traditional, contemporary, and emerging technologies. Using an engineering design process, children experience opportunities to generate solutions to real-life problems through playful experimentation and investigation. Scientific inquiry enables children to develop an interest in and understanding of the biological, material, and physical world by exploring and investigating scientific concepts and processes.
Wellbeing supports children’s social, emotional, and physical development now and into the future. It enables children to develop self-awareness and knowledge, build life skills, and develop a strong sense of connectedness to their school, their community, and wider society. To develop these skills and dispositions, it is important for children to develop their own ethical understanding of the world. Values education encourages reflection on choices, exploration of opportunities, and commitment to responsibilities. Children will be encouraged to value what it means to be an active citizen, with rights and responsibilities, in local and wider contexts. Wellbeing provides structured opportunities for children to be as physically and emotionally well and healthy as they can be. This happens by building their motivation and commitment to physical activity and to inform healthy lifestyle choices. Wellbeing also supports children to value positive and healthy relationships with others, which includes acquiring an understanding of human sexuality that is balanced and connected with the relational and emotional aspects
A broad experience in the arts is integral throughout a child’s experience in primary school. The arts give expression to and extend children’s understanding, imagination, and creativity through a broad range of experiences. Such experiences have the capacity to engage, inspire, and enrich all children, exciting the imagination and encouraging them to reach their creative and expressive potential. Art, Drama, and Music provide opportunities for broad-ranging experiences in the arts, including visual arts, media arts, and dance, that play a valuable role in children’s experience of childhood. Such experiences help them to participate fully in their community and in society as a whole. While Art, Drama, and Music have a common creative process and share transferable skills, each has its own knowledge, concepts, skills, and intrinsic value. By drawing on more than one subject, learning in other art forms can be enhanced and developed through an integrated approach to Arts Education.
Social and Environmental Education contributes to children’s understanding and development of the interconnected historical, geographical, and societal dimensions and processes of life. It supports children’s awareness, appreciation, and understanding of the world through learning about the rich diversity of peoples: their experiences, cultures, religions, beliefs, and environments in different times, places, and circumstances. It helps children to develop an understanding of the human and natural environments and the relationship between them. Through Social and Environmental Education, children develop the attitudes, concepts, dispositions, knowledge, skills, and values that motivate and empower them to become informed and active citizens who promote a more sustainable future. This is made more meaningful and empowering through children’s active identification, exploration, and investigation of local, national, and global challenges and opportunities, past and present. Hence, children come to an understanding and appreciation of their inherent rights and responsibilities as custodians of this planet.
The Primary Curriculum Framework outlined suggested time allocations for each curriculum area and subject. Time allocations comprises two categories: Minimum Curriculum Time (weekly and monthly) and Flexible Time (monthly). Minimum Curriculum Time provides a weekly minimum time allocation for Language, Mathematics, and Wellbeing and a monthly (based on a period of four weeks) minimum time allocation for Science, Technology, and Engineering Education; Social and Environmental Education; and Arts Education. The time allocations are intended to be used flexibly, in order to embrace integrative learning, avail of unexpected learning opportunities, pace learning in response to children’s needs, and support immersive and engaging learning experiences.
